翻譯高階語言成機器語言-編譯器與直譯器
有兩種方式將人類所撰寫的是 source code 翻譯電腦能夠看得懂的是 machine code:編譯器或直譯器。
編譯器
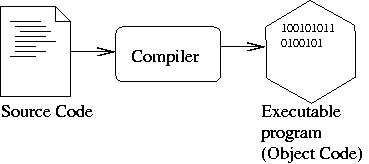
- Source code 在 compile time 被 編譯成 machine code ,然後在 runtime 被執行。
- Runtime 時不進行 parse(or syntactic analysis,語法分析),執行效率較快速。
- 每次的執行是一支程式,執行編譯過後的執行檔來執行程式。
- 若是程式中存在語法錯誤,則程式會無法通過編譯,整支程式都無法執行。
- 無法即時測試局部的程式,除錯速度通成較慢。
- 使用編譯器的語言包括 C/C++, Fortran, Java, rust, go…
Source code in C:
1 | printf("hello world\n") //executable |
Output:
1 | 識別項\"pppprintf\" 未定義 C/C++(20) |
直譯器

- Source code 在 runtime 被直譯。
- Runtime 時進行 parse,執行效率較緩慢。
- 每次的執行是一行程式,不會產生額外的檔案。
- 若是程式存在語法錯誤,則程式會執行到語法錯誤的那行程式碼才會無法繼續。
- 可以即時測試局部的程式,除錯速度通成較快。
- 使用直譯器的語言包括 Python, Matlab, Bash, Lisp,Pascal, BASIC…
Source code in bash:
1 | ~$ echo hello world && echoooo hello world #executable && syntax error |
Output:
1 | hello world #executable |
Note
有時候可見某個語言被分類為「編譯語言」或是「直譯語言」(e.g, C語言是編譯語言),但這樣的描述並不全然正確,不經過任何轉換,程式碼也僅是文字檔。一個語言是「編譯」或是「直譯」的理由並不源自語言本身,而是傳換成被電腦理解的過程;而一個幾乎使用的編譯器的語言(e.g, C語言),也可以藉由直譯器來實現。
參考資料:
Understanding Python Bytecode | Interpreter (computing) | Compilers vs Interpreters – An overview of the differences | Difference between CPython, Jython, IronPython, PyPy, and Cython